These five pictures are taken from the second chapter of the Guidance Atlas of Building Photovoltaic System Design. The pictures include the types of photovoltaic systems, the design points of photovoltaic systems, the grid access requirements and schematic diagrams of grid-connected systems, off-grid system design diagrams, and schematic diagrams of photovoltaic storage direct and flexible systems.
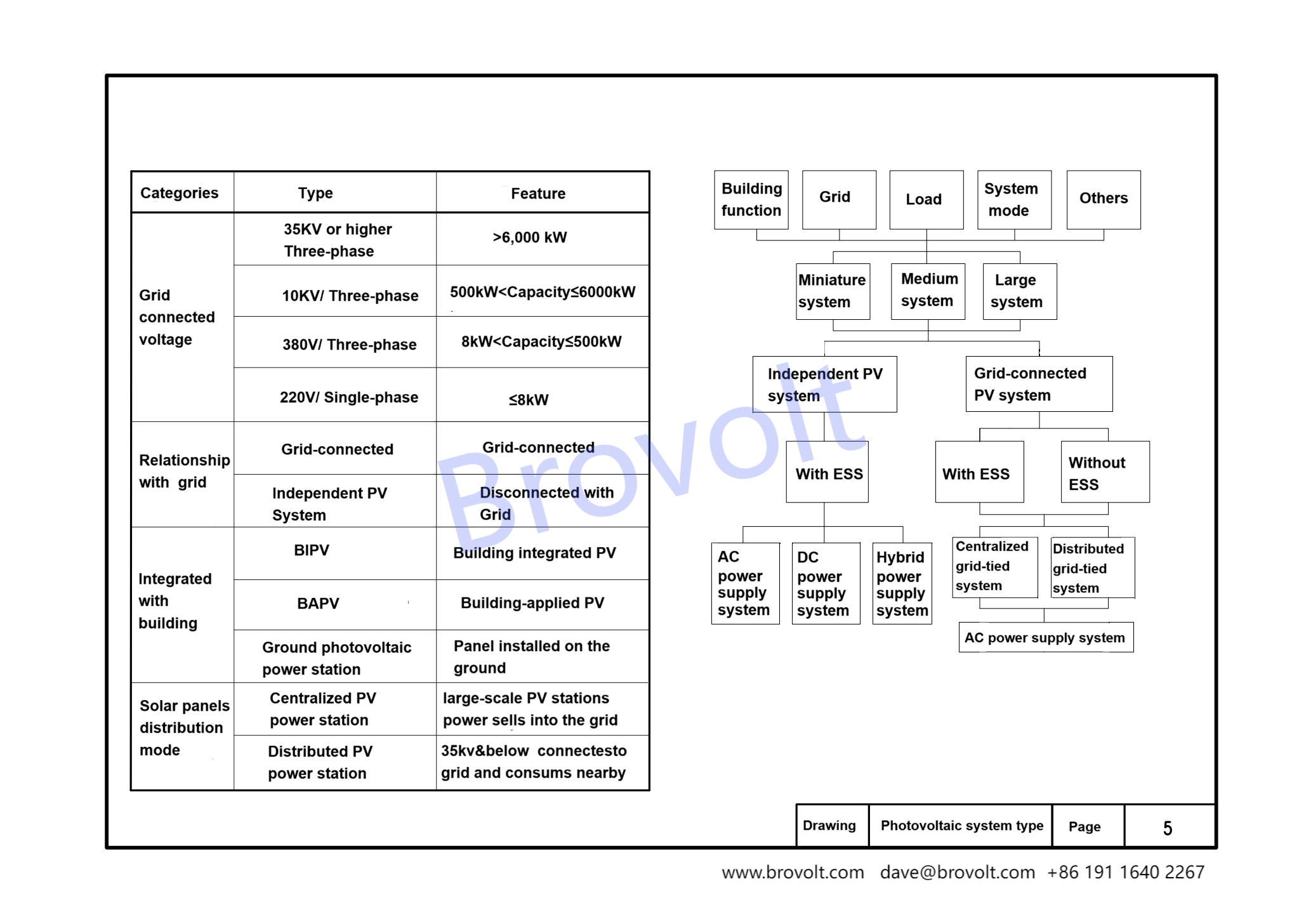
1. The types of photovoltaic systems can be divided into 35KV and above, 10KV, 380V, and 220V according to the grid-connected voltage level. The corresponding installed capacities are respectively installed capacity greater than 6000kW, installed capacity greater than 500kW, installed capacity less than or equal to 6000kW, installed capacity greater than 8kW, installed capacity less than or equal to 500kW, and installed capacity less than or equal to 8kW.
The types of photovoltaic systems can be divided into off-grid photovoltaic systems and grid-connected photovoltaic systems according to whether they are connected to the grid.
The types of photovoltaic systems are divided into building integrated photovoltaic systems (BIPV), building attached photovoltaic systems (BAPV), and ground photovoltaic power stations (components installed on the ground or on structures) according to the combination mode with buildings.
The types of photovoltaic systems can be divided into centralized photovoltaic power stations and distributed photovoltaic power stations according to the distribution mode of photovoltaic components.
Centralized photovoltaic power stations are mainly used for centralized construction of large-scale photovoltaic power stations to generate electricity directly connected to the public power grid. Distributed photovoltaic power stations are mainly used for access to voltage levels of 35kV and below, and for nearby consumption.
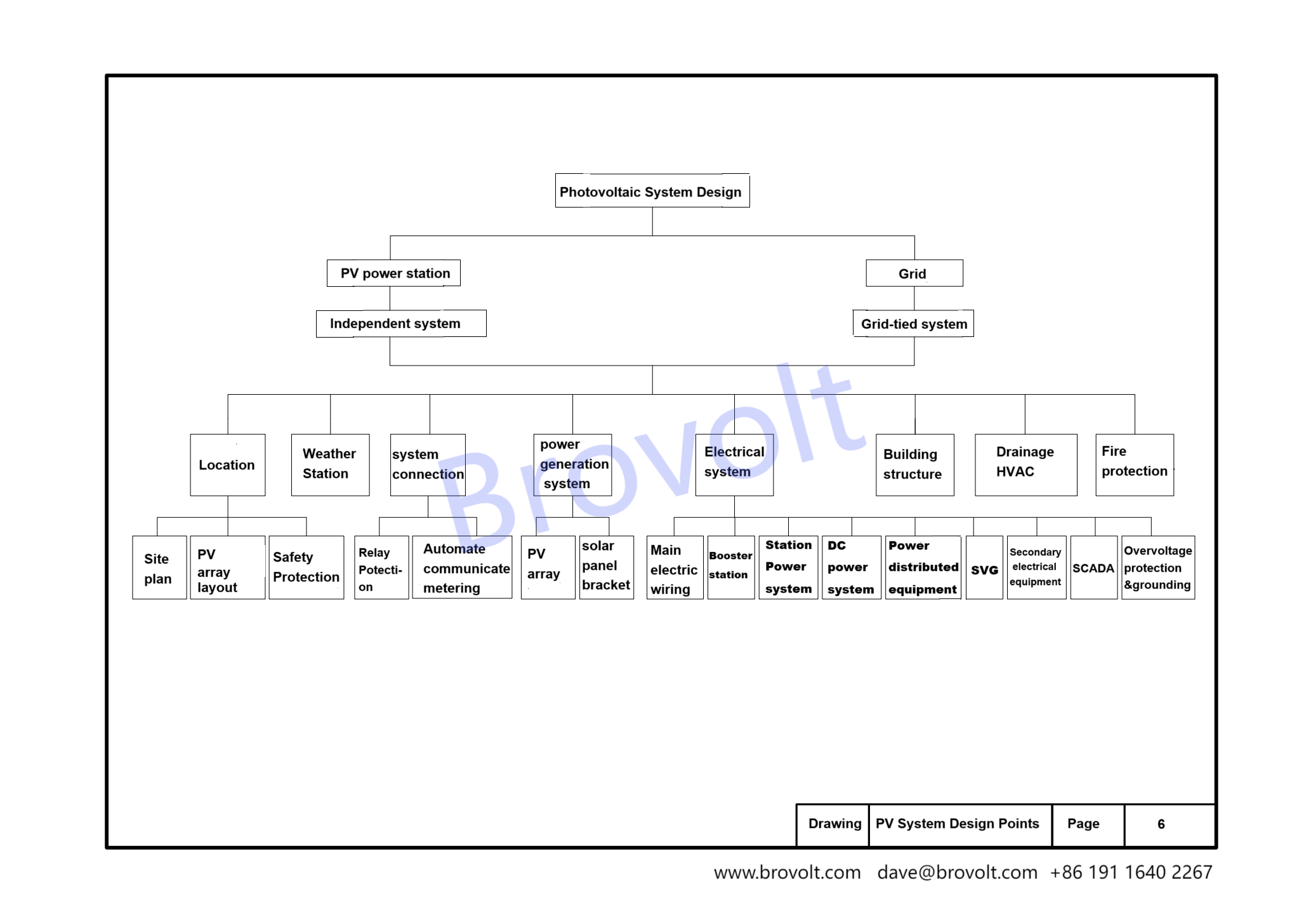
2.Photovoltaic system needs to be considered comprehensively in design. When designing, it is necessary to consider the layout of the photovoltaic power station, the meteorological station, the connection system with the load and the power grid, the power generation system, the electrical system, the building structure, solar panels,the water supply and drainage, the HVAC, and the fire protection system. For the photovoltaic power station, we need to draw a general plan, plan the layout of the photovoltaic array, and take safety and protection measures for the photovoltaic power station. Access system needs to consider the power system relay protection, automation, communication, and power metering. Power generation system needs to consider the selection of photovoltaic panels and photovoltaic brackets.
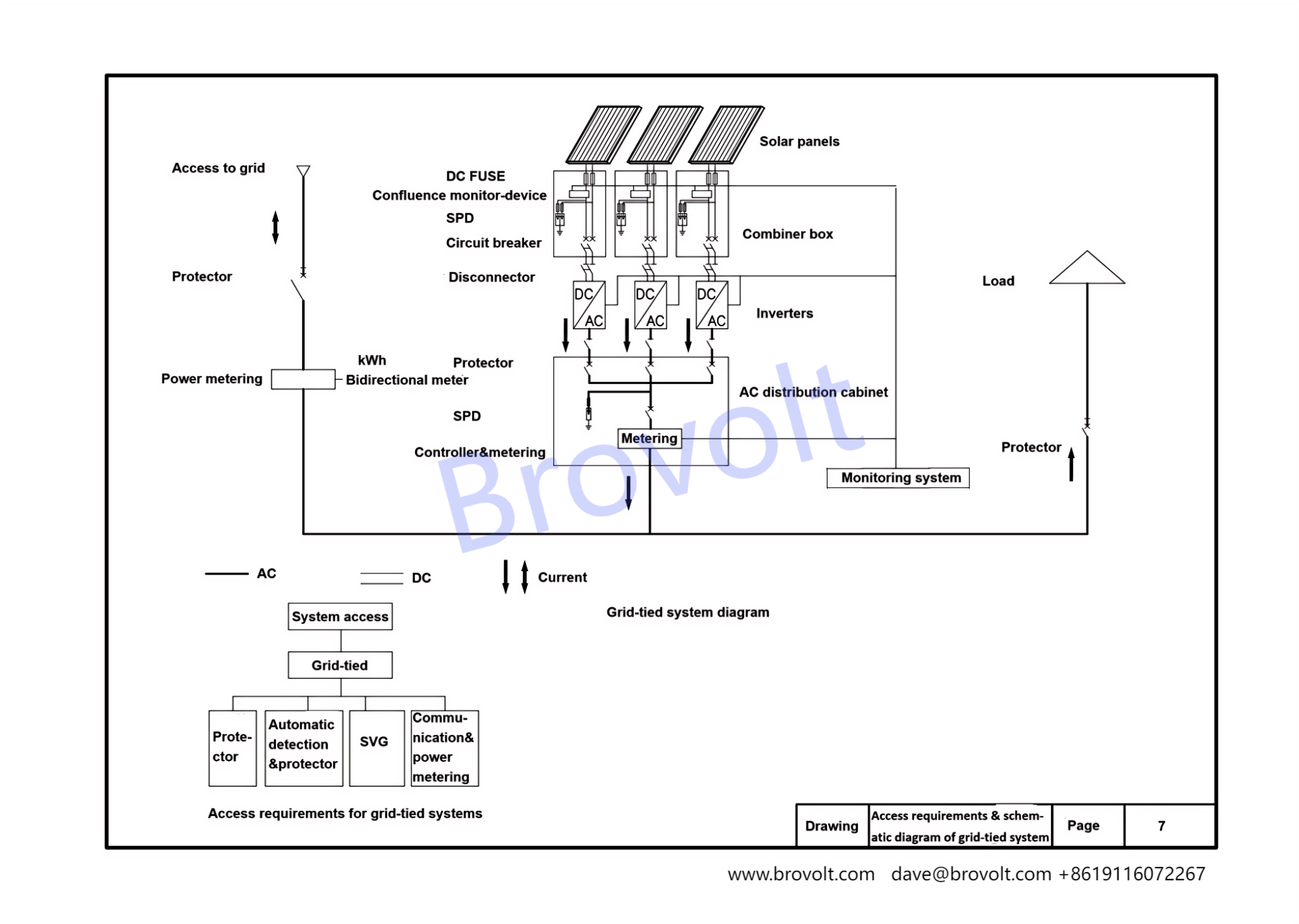
3. Requirements and schematic diagrams for access to the power grid for photovoltaic grid-connected systems Power system relay protection, automatic protection device, reactive power compensation device, communication and power metering device. When designing the entire system, photovoltaic components. Corresponding equipment needs to be added. Common ones include DC fuses, DC surge power device, confluence monitoring devices, circuit breakers, disconnectors, protection devices, AC surge power device, metering devices, combiner boxes, AC distribution cabinets, and inverters.
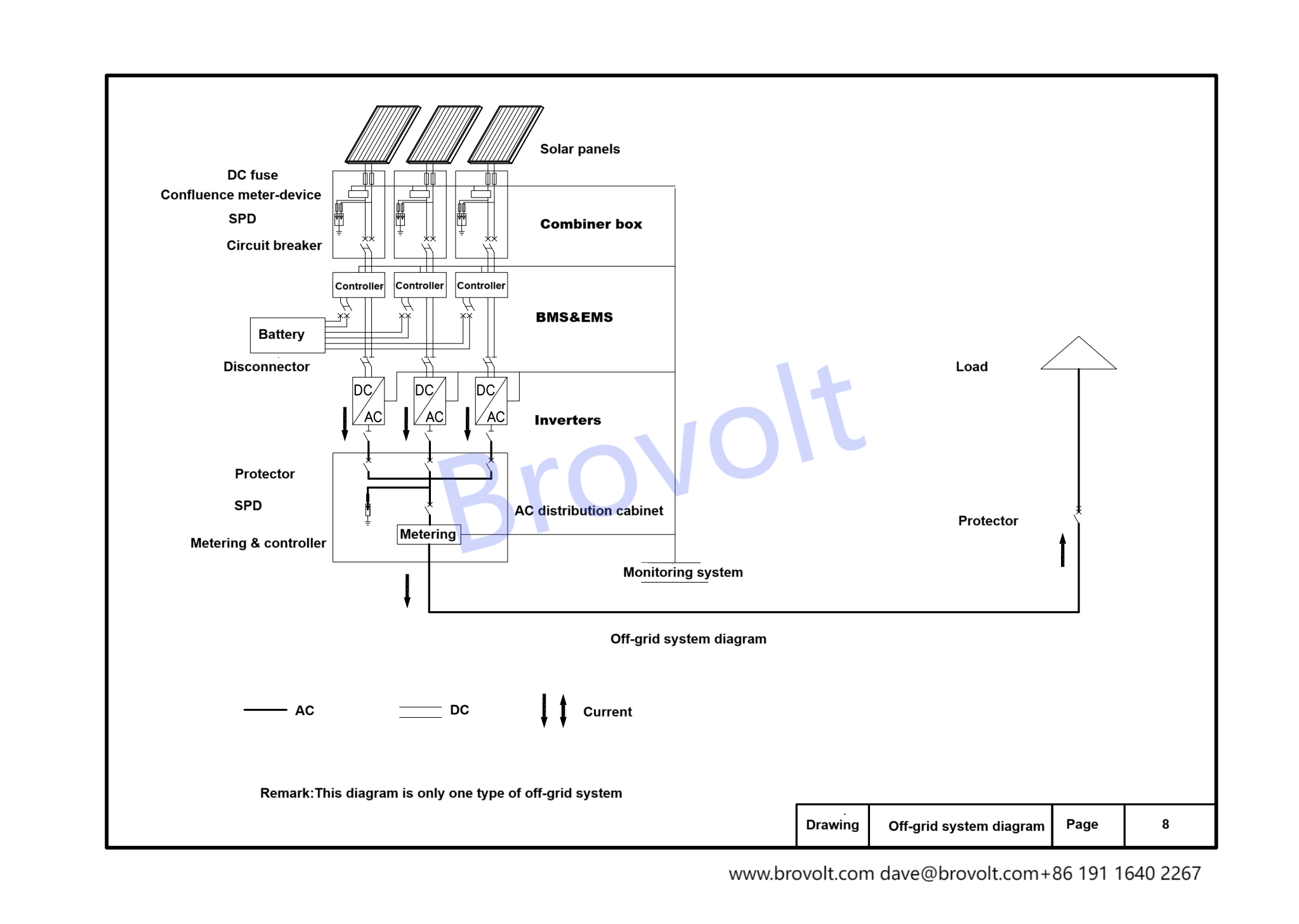
4. Schematic diagram of off-grid system
When designing the entire system, photovoltaic components. Corresponding equipment needs to be added. Common ones include DC fuses, DC surge power device, confluence monitoring devices, circuit breakers, energy storage systems, EMS, BMS, disconnectors, protection devices, AC surge protectors, metering devices, combiner boxes, AC distribution cabinets, and inverters.
5.Photovoltaic Energy Storage Direct Current Flexible (PEDF)
Photovoltaic power generation on the roof of the building is connected to 375V DC bus through a DC/DC (DC to DC converter).
DC bus is connected to the energy storage system through DC/DC, and the charging piles connected by this DC bus are arranged in the adjacent parking lot, and the electric vehicles in the parking lot are charged through these charging piles.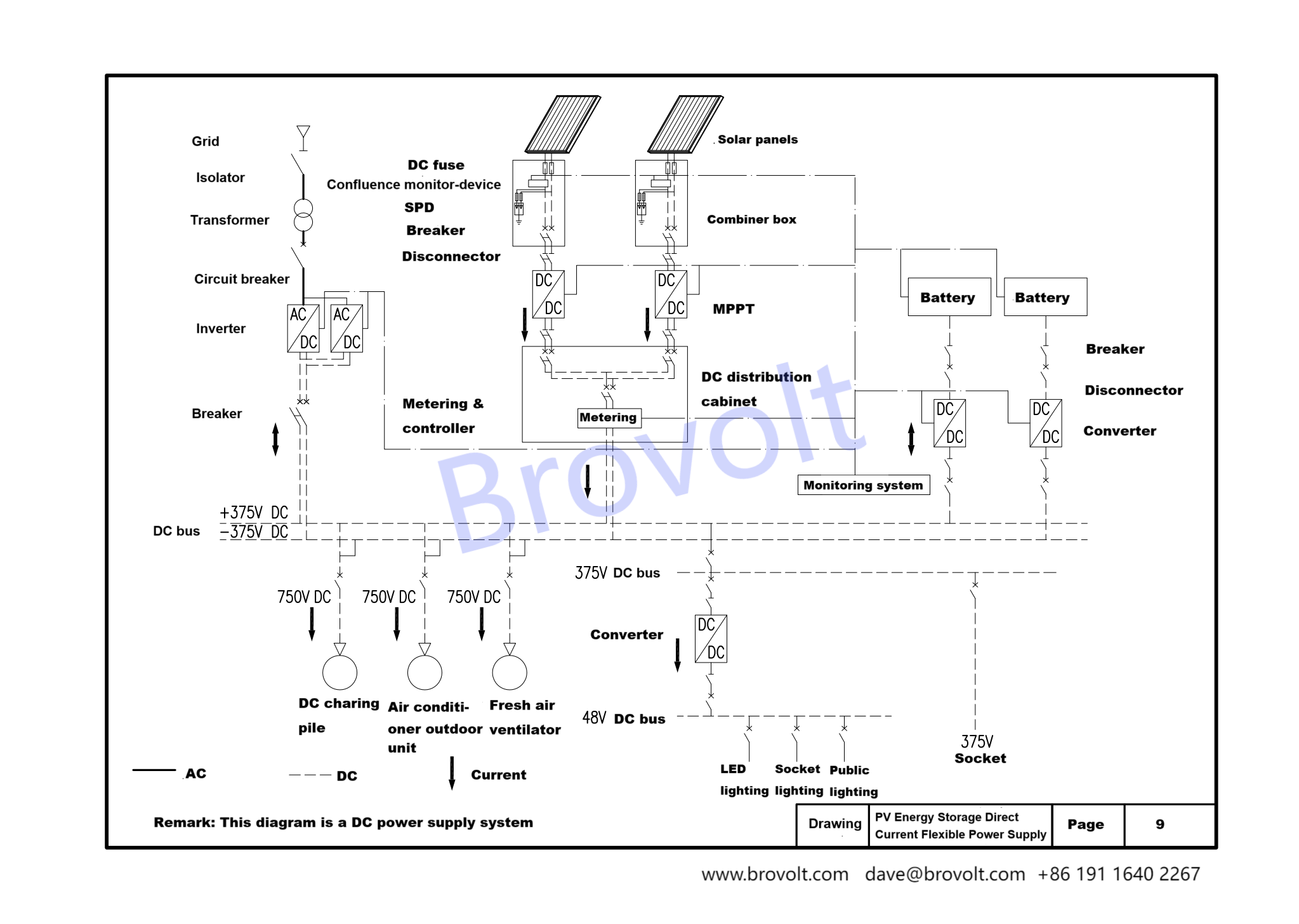
This system adopts a DC power supply system, including 375V DC for power and charging equipment, and a 48V DC branch for small power appliances obtained through DC/DC conversion. The 375V DC bus is connected to the AC 380V power grid through an AC/DC (AC to DC converter), and the power is input from the external power grid to meet the power demand of the building.
For the power grid, this system is not a rigid load that the power supply must be equal to the power consumption on the load side at this time, but the power taken from the power grid can be adjusted within a large range according to the supply and demand relationship of the power grid. From the perspective of the power grid, this power consumption system becomes a flexible load of the power grid.